 It is critical for OEMs to build innovative cybersecurity features to counter emerging threats and keep consumer trust, and recent ASHB research sets out a measured approach for manufacturers and others to collaborate, assess cyber risks and support market-wide solutions.
It is critical for OEMs to build innovative cybersecurity features to counter emerging threats and keep consumer trust, and recent ASHB research sets out a measured approach for manufacturers and others to collaborate, assess cyber risks and support market-wide solutions.
ASHB’s Privacy and Cybersecurity in the Connected Home focused in particular on understanding the implications of cybersecurity and privacy risks and ways to manage them. It reviewed the challenges of implementing protection measures, and evaluated the perceptions of various industry stakeholders—including their level of accountability in managing the challenges. The analysis also suggested best practices that should be prioritized to address cybersecurity.
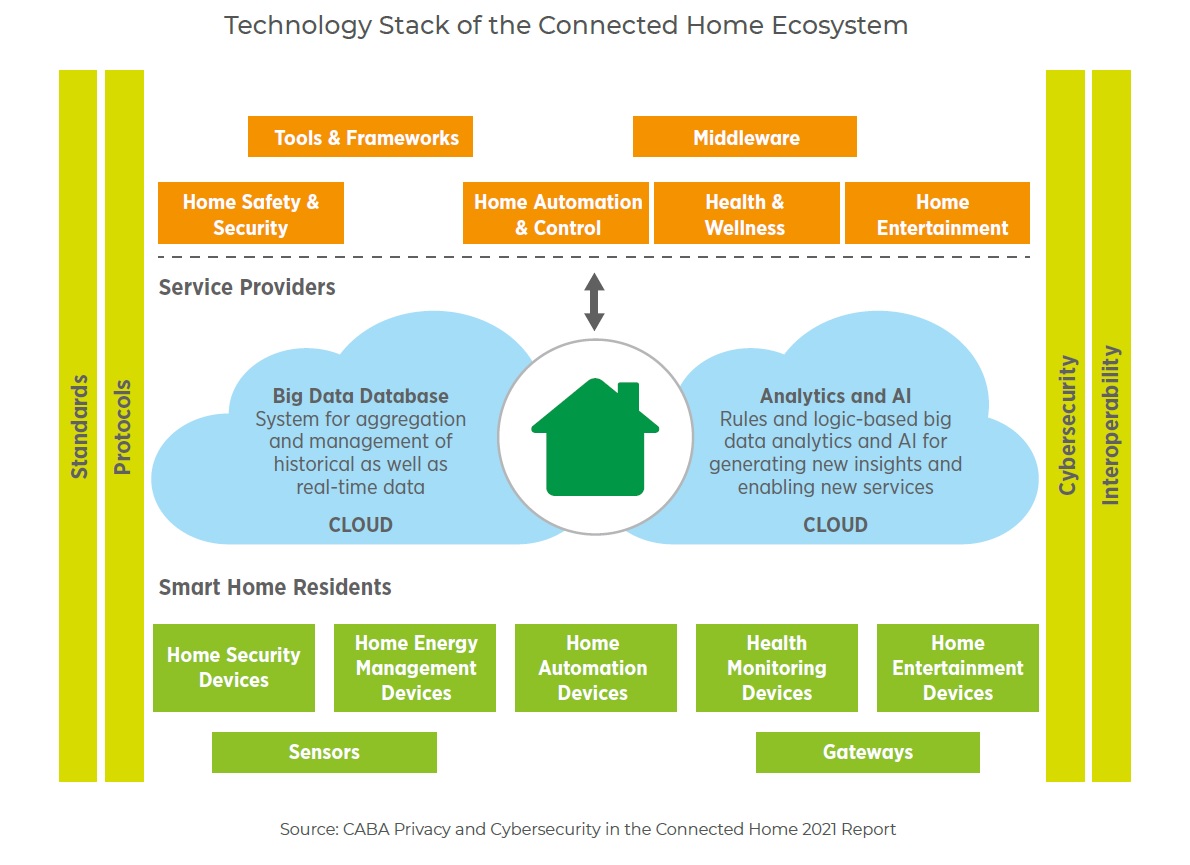
Perhaps the key underlying factor giving rise to cyberthreats, the report highlights, is the growth in the technology layer that makes up the vast smart-home ecosystem. It includes three broad areas of concentrated activity. Solution providers are involved within the home; within the interlinked layer that joins the home to the external world; and/or within the remote layer housing activities in the cloud. In-home applications deal with local applications embedded in devices and/or a gateway. Connected-home device manufacturers and home automation specialists provide either ad-hoc smart home subsystems or whole home solutions. Taking place in the the interlinked layer are activities between the home and the external world, which may include the interface between a residential gateway and a remote service platform. It is typically dominated by communication infrastructure providers, Internet service providers (ISPs), and other technology platform providers that support abstraction of services and solutions for the connected home. Hosting and aggregation of remote applications and services take place in the cloud. The applications interface there with service platforms, bridges, and control hubs to control and operate home devices.
The growing connected-home ecosystem and expanding technology stack are increasing the potential for various vendors and service providers to inflict security breaches on each other’s networks. ASHB’s report dives into the implications of cybersecurity and privacy risks and ways of managing them. It reviews the challenges of implementing protection measures and evaluated the perceptions of various industry stakeholders—including their level of accountability in managing the challenges. The analysis also provided best practices that can be prioritized to address the issue.
Dynamic response plan
With a projected continued evolution in cyber threats, a dynamic response is required of key industry participants. Privacy is also a changing concept as consumers are introduced to novel experiences with emerging technologies and service experiences, the report notes. It is likely that expectations from vendors will shift as consumers weigh functionality, usefulness, and compromises to their privacy and anonymity.
For vendors and service providers, it is important to chart out a nimble and scalable response plan that can cope with their growth needs and consumers’ evolving demands for new connected products and solutions, the report recommends.
The research calls on solution providers to enhance their compliance levels, given the growing consumer sophistication and vigilance regarding the use of their devices and their expanding expectations of cybersecurity and privacy. But instituting prescriptive cybersecurity requirements and minimum privacy provisions in products requires collaboration between alliances and standards-development bodies to ensure that interoperability and cyber compliance is achieved consistently.
What remains to be seen is how much of this compliance can be institutionalized and mandated. As the report notes: “Interdependencies and crossover impacts will continue to challenge regulators, assimilators, integrators, aggregators, and above all, consumers. Adopting some of the best practices described in this research will help support the compliance agenda and fast-track the consensus needed to address cybersecurity and privacy challenges.”



